What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a common type of eczema caused by the skin’s inflammatory reaction after coming into contact with external substances. Patients may develop eczema symptoms after using metal jewelry, herbal patches, hair dyes, or skincare products – these all fall under the category of contact dermatitis.
Why Do Skincare Products or Metals Cause Contact Dermatitis?
There are two common types of contact dermatitis:
Allergic contact dermatitis – caused by the body’s immune system reacting with hypersensitivity to specific external substances like metals or hair dye ingredients. Irritant contact dermatitis – caused by skin cells being directly irritated by acute or prolonged exposure to external irritants. Highly concentrated alpha hydroxy acid in skincare, dish soap, cleansers, chemical solvents, or synthetic fragrances can all trigger irritant contact dermatitis. Hand eczema is a common example. The more exposure, the more severe the symptoms tend to be. Of metal jewelry, the nickel found in inexpensive jewelry is the most common allergen. Other metals like iron, copper, cobalt, and chromium can also cause allergies. For hair dyes, those containing paraphenylenediamine (PPD) are most likely to trigger allergies, especially in allergy-prone individuals.
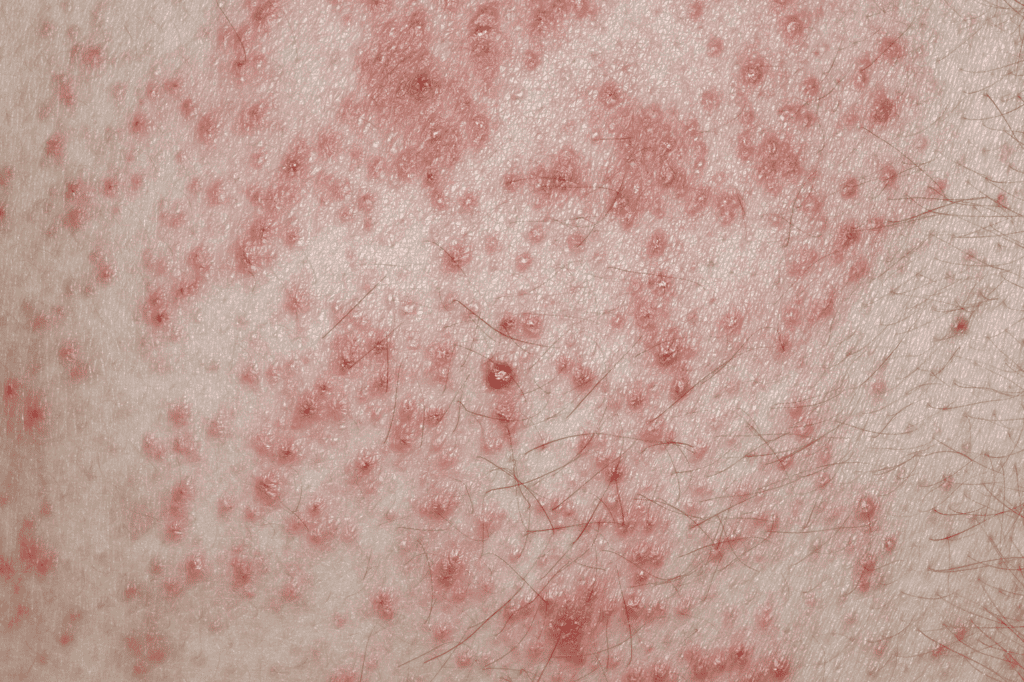
What Are the Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis and How to Identify Them?
Allergic contact dermatitis symptoms tend to be more severe, with blisters, oozing of fluid, redness, and intense itching at the affected area. Most patients experience worsening symptoms over time.
While less severe than the allergic type and typically without blisters, irritant contact dermatitis can still cause redness, peeling, and sometimes unbearable itching of the affected skin.
For facial contact dermatitis, the main trigger is usually a reaction to new facial cleansers/soaps, skincare, or makeup products causing irritation or allergy. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and itching. Once these symptoms appear, immediately stop using any newly introduced facial products and only use gentle, familiar moisturizers.
Mild cases usually resolve within days, while severe cases require topical steroid creams and oral antihistamines for about a week to resolve. Since skincare and makeup contain complex ingredients, it can be difficult to pinpoint the culprit. Those with sensitive skin should patch test new products on their inner arm for 5 days before using on the face.
How to Prevent Contact Dermatitis?
The key to preventing contact dermatitis is identifying potential triggers and avoiding contact with those substances. Blood tests or skin patch testing can help diagnose individual allergens, though results may not be fully accurate due to the complexity of allergies and require interpretation along with personal experience.
How to Treat Contact Dermatitis?
Treatment depends on the severity, but generally involves oral medications and topical creams:
During acute flare-ups, doctors prescribe topical steroid creams to reduce inflammation and itching when applied to affected areas. Patients can self-treat with cold compresses for 10-15 minutes, 3-4 times a day to relieve inflammation and itch. For severe symptoms, oral medications may be needed for 2-3 days to improve the condition.
What If Skin Remains Sensitive After Treatment?
Some people experience persistent skin sensitivity to any skincare or makeup products after an episode of irritant contact dermatitis. This may indicate allergic contact dermatitis, which would require the doctor to evaluate if a patch test is needed to identify allergens.
If not allergic, the patient should temporarily avoid all cleansers and skincare, using only gentle petroleum jelly for moisturizing. Once the skin has normalized, slowly reintroduce regular products while monitoring for any sensitivity.
If you want to know more, or want to browse more pictures, please click the video below: