What is a furuncle? What is its relation to folliculitis?
A furuncle, colloquially known as a “seed”, is an acute suppurative inflammatory skin disease centered on a hair follicle. It is closely related to folliculitis, as they are both infectious inflammatory reactions of the hair follicles and surrounding tissues, differing only in depth and extent of involvement.
The main cause of furuncles is infection by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus, which enter the dermis layer through small skin abrasions or hair follicles. Once infected, the immune system is immediately activated, with a massive influx of white blood cells forming a localized abscess of pus accumulating inside or around the hair follicle, resulting in inflammation, swelling, pain, and fever.
What are the symptoms of a furuncle?
The typical symptoms of a furuncle are:
Occurs in hair-bearing areas like the scalp, face, armpits, groin, etc. Begins as a small red bump that gradually enlarges into a hard, red, swollen, painful mass. After a few days, the mass softens with a yellow or pale green pustule forming in the center. Once the furuncle ruptures and drains pus and blood, the pain subsides. Often leaves a temporary scar or discoloration after rupturing. Systemic symptoms like low-grade fever, headache, chills indicate a widespread inflammatory response. If a furuncle is not properly drained in time, the infection can spread to the lymphatic vessels and bloodstream, causing complications like lymphangitis and lymphadenitis.
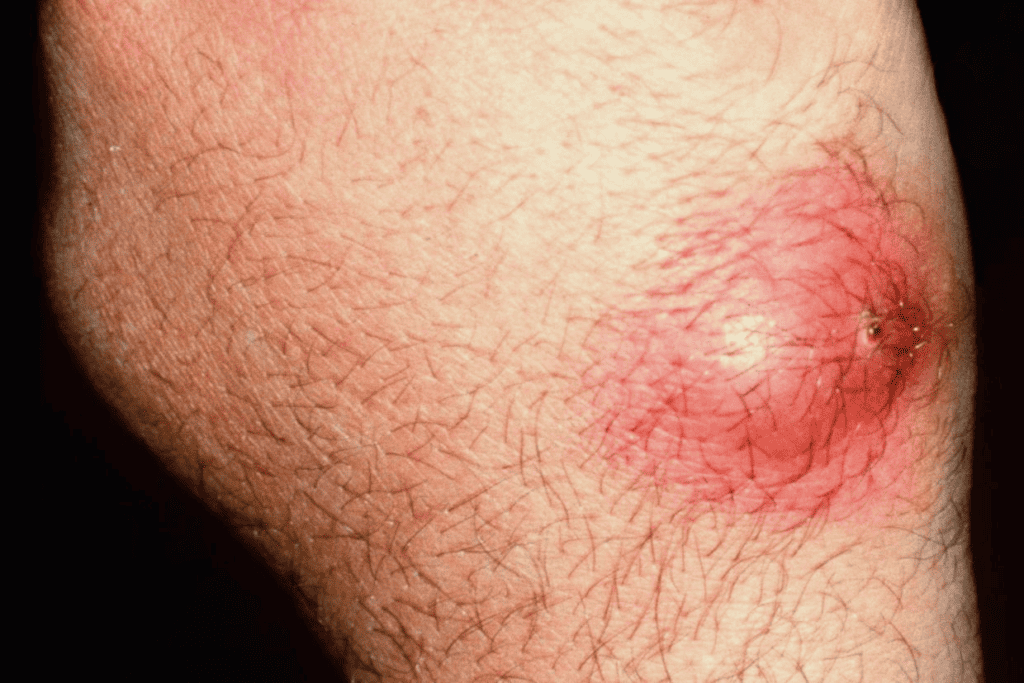
How should a furuncle be managed?
Once furuncle symptoms appear, seek medical attention immediately and follow these care steps as advised:
Keep the affected area clean and dry, washing with warm water or saline and applying disinfectant. Do not squeeze or puncture the pustule to avoid worsening the infection or spreading bacteria. Apply warm or cold compresses to relieve pain and promote drainage. Take oral antibiotics or apply topical ointments as prescribed. For larger abscessed furuncles, the doctor may need to make an incision and drain the pus under sterile conditions. If complications develop, seek aggressive treatment, potentially requiring intravenous strong antibiotics. Get adequate rest, maintain a balanced diet, and support the body’s immune defenses.
What complications can arise from furuncles?
If furuncles are not treated promptly and effectively, bacteria can spread to the lymphatic system and bloodstream, leading to complications such as:
Lymphangitis – redness, pain, and swelling along the lymphatic vessels. Lymphadenitis – swelling and inflammation of nearby lymph nodes. Cellulitis – infection spreading to subdermal tissues, causing severe redness, swelling, heat, and hardening. Bacteremia – bacteria entering the bloodstream, causing fever, chills, and systemic symptoms. Meningitis, endocarditis, etc. – in rare cases may spread to brain membranes or heart valves. Furunculosis – recurrent outbreak of multiple furuncles, common in diabetics or immunocompromised. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical treatment at the first signs of a furuncle to prevent worsening or complications.
What if a furuncle develops on the face?
A furuncle on the face, colloquially known as a “facial yen”, is considered more problematic. Due to the rich vasculature, lymphatics, and extensive venous networks in the face and head area that connect to the intracranial venous sinuses, any facial infection risks rapidly spreading into the skull, potentially causing serious complications like meningitis, brain abscess, or septic venous thrombosis.
So if a facial furuncle develops, do not delay treatment. Remember:
Do not squeeze or rupture the facial furuncle. If widespread facial redness, swelling, fever, or headache develops, seek immediate medical evaluation. Severe facial furuncles often require hospitalization for intravenous high-potency antibiotics and drainage procedures. Seek specialist care immediately if any neurological symptoms like altered consciousness or visual problems arise. Facial infections demand prompt medical attention and should never be ignored.
If you want to know more, or want to browse more pictures, please click the video below: